BECE 2002 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The gas usually used in fire extinguishers is
Solution: Carbon dioxide is commonly used in fire extinguishers because it displaces oxygen, smothering the fire and preventing combustion without leaving residue.
2. The physical change(s) that take(s) place when a piece of ice is heated continuously for a long time can be represented by
Solution: Heating ice first melts it to liquid water (solid→liquid), then boils the water to steam (liquid→vapor), following sequential phase changes.
3. The chemical formula \( H_2 \) represents
Solution: \( H_2 \) denotes a diatomic molecule of hydrogen, composed of two chemically bonded hydrogen atoms.
4. The dissolution of sugar in water is a physical change because the sugar
Solution: Physical changes are reversible; sugar dissolved in water can be recovered unchanged via evaporation, confirming no chemical reaction occurred.
5. Which of the following statements is true at the boiling point of water?
Solution: During boiling, absorbed heat energy breaks intermolecular bonds for phase change rather than raising temperature, maintaining a constant temperature.
6. When matter changes state from gas to liquid there is
Solution: Condensation (gas→liquid) reduces particle spacing, decreasing volume while mass remains conserved.
7. The energy possessed by a compressed spring is a
Solution: Stored energy due to the spring's deformed position (mechanical stress) is elastic potential energy.
8. A ball is dropped from a height to the ground. The energy possessed by the ball just before it strikes the ground is called
Solution: At impact, gravitational potential energy is fully converted to kinetic energy due to motion.
9. Which of the following statements about a force are true?
I. It causes moving objects to stop
II. It causes stationary objects to move
III. It can change the direction of motion
IV. It can change the shape of an object
Solution: Force fundamentally alters motion (Newton's laws: starting/stopping/changing direction) or deforms objects (e.g., compression).
10. A body of mass 50 kg falls through a height of 5m. If the acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms\(^2\), calculate the loss in potential energy.
Solution: Loss in PE = mgh = 50 kg × 10 m/s² × 5 m = 2500 J.
11. Which of the following substances can be used as an electrical insulator?
Solution: Plastic lacks free electrons, preventing electrical conduction, unlike metals (copper, zinc) or semi-metals (graphite).
12. Gaps are left between railway lines to
Solution: Gaps accommodate thermal expansion of rails in heat, preventing buckling or deformation.
13. A beak and claws are protective structures of a
Solution: Hawks use sharp beaks and talons (claws) for defense and hunting, unlike crabs (pincers), lions (claws), or snakes (fangs).
14. An example of a parasite which lives in the intestines of an animal is
Solution: Tapeworms reside in host intestines, absorbing nutrients directly, unlike guinea worms (subcutaneous) or plasmodium (blood).
15. The best way to prevent guinea worm disease is by
Solution: Boiling kills copepods (water fleas) carrying guinea worm larvae, eliminating the transmission vector.
16. Malaria parasites enter the human body through
Solution: Infected female Anopheles mosquitoes inject Plasmodium parasites during blood-feeding.
17. Human beings are omnivorous because they eat
Solution: Omnivores consume plant- and animal-derived foods, a key dietary classification.
18. The characteristics that distinguish living things from non-living things is that, living things
Solution: Autotrophy (e.g., photosynthesis) is exclusive to living organisms; non-living entities cannot produce their own nutrients.
19. Animals depend on plants for food because
Solution: Plants are primary producers (via photosynthesis), forming the base of food chains; animals lack this capability.
20. Which of the following animals has a body temperature which changes with the temperature of the surroundings?
Solution: Toads are ectothermic (cold-blooded), relying on external heat to regulate body temperature, unlike birds (crow) or mammals (rabbit).
21. The farming practice which would improve soil fertility is
Solution: Crop rotation replenishes soil nutrients (e.g., legumes fix nitrogen) and disrupts pest cycles.
22. The best soil for plant growth consists of correct proportions of
Solution: Loam soil (clay+sand+humus) balances drainage (sand), water retention (clay), and nutrients (humus).
23. The by-product of photosynthesis is
Solution: Photosynthesis consumes CO₂ and H₂O to produce glucose and release oxygen as waste.
24. Blood circulates to all parts of the human body with the help of the
Solution: The heart pumps oxygenated blood via arteries and receives deoxygenated blood via veins.
25. The end-product of the digestion of carbohydrates is
Solution: Enzymes (e.g., amylase) break down complex carbohydrates (starch) into simple sugars like glucose.
26. The central nervous system is made up of the
Solution: The CNS integrates sensory input and coordinates responses via the brain and spinal cord; nerves are peripheral.
27. Which of the following organs are used for excretion?
I. Lung
II. Skin
III. Kidney
IV. Heart
Solution: Lungs (CO₂), skin (sweat), and kidneys (urine) eliminate waste; the heart circulates blood but doesn’t excrete.
28. The plant structures used for gaseous exchange are the
Solution: Stomata on leaf surfaces facilitate CO₂/O₂ exchange during photosynthesis and respiration.
29. Digestion of starch in humans starts from the
Solution: Salivary amylase in the mouth initiates starch breakdown into maltose.
30. The male sex cell is the
Solution: Sperm (haploid gamete) fertilizes the female egg; testis produces sperm but is not the cell itself.
31. Which of the following seeds is dispersed by explosive mechanism?
Solution: Okra (Okro) fruits dry and split open violently, ejecting seeds away from the parent plant.
32. The ear is the organ for detecting
Solution: The ear converts sound waves into nerve impulses via the cochlea for auditory perception.
33. Which of the following substance is a digestive juice?
Solution: Bile (produced by the liver) emulsifies fats in the duodenum, aiding lipid digestion.
34. An example of a disease transmitted through air is
Solution: Measles spreads via airborne respiratory droplets from infected individuals.
35. Which of the following diseases can be caused by a housefly?
Solution: Houseflies transmit dysentery-causing pathogens (e.g., Shigella) by contaminating food with feces.
36. The part of the body of an animal that is usually affected by tuberculosis is the
Solution: Mycobacterium tuberculosis primarily infects lung tissue, causing pulmonary TB.
37. The irregular emptying of the bowels is the cause of
Solution: Constipation results from infrequent bowel movements, leading to hardened stool and straining.
38. The farther away a planet is from the sun, the
Solution: Solar radiation intensity decreases with distance (inverse-square law), reducing surface temperature.
39. The instrument used to measure relative humidity is the
Solution: Hygrometers measure atmospheric moisture content (relative humidity) using materials sensitive to humidity changes.
40. How many days does the moon take to go round the earth?
Solution: The sidereal month (orbital period relative to distant stars) is approximately 27.3 days.
1. QUESTION 1
1. (a) Name four characteristics of non-living things.
(b) Mention two functions of each of the following parts of a plant:
(i) leaves
(ii) roots
(c) Classify the following actions as voluntary or involuntary:
(i) eating
(ii) walking
(iii) sneezing
(iv) laughing
(d) (i) Explain the difference between a physical change and a chemical change.
(ii) Write down the chemical equation for the preparation of carbon dioxide in the laboratory.
(e) (i) What is a machine?
(ii) Write down an expression for the efficiency of a machine.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1.(a)
- They do not respire
- They do not excrete
- They do not feed
- They do not grow
- They do not reproduce on their own
- They do not respond to stimuli on their own
- They do not move on their own
(b) (i) Functions of leaves:
- Photosynthesis (preparation of food using carbon dioxide and water)
- Transpiration (loss of water vapour through the stomata)
- Respiration (intake of oxygen to produce energy)
- Guttation (oozing out of excess water from the surface of leaf)
- Food storage in certain leaves
(ii) Functions of roots:
- Absorbs water and mineral salts from the soil
- Some roots store food prepared by the plant
- Holds the plant firmly in place
(c) (i) eating - voluntary
(ii) walking - voluntary
(iii) sneezing - involuntary
(iv) laughing - voluntary
(d) (i)
- Physical change: No new substance is formed and it is reversible
- Chemical change: A new substance is formed and it is irreversible
(ii) CaCO₃ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂
(e) (i) A mechanical device that makes work easier and/or faster
(ii) Efficiency = (Work output / Work input) × 100%
OR(Mechanical Advantage / Velocity Ratio) × 100%
2. QUESTION 2
2. (a) (i) Mention four female sexual characteristics of a human being.
(ii) Name two sense organs in mammals.
(iii) Give one function of each of the sense organs named.
(b) Define each of the following terms:
(i) compound
(ii) element
(c) List the particles that make up an atom.
(d) State the energy changes that take place in each of the following processes:
(i) An orange falls from a tree to the ground
(ii) A carpenter hits a nail with a raised hammer.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2.(a) (i) Female sexual characteristics:
- Ovaries
- Womb
- Fallopian tube
- Cervix
- Vagina
- Vulva
- Menstruation
- Ovulation
- Broader hips
- Larger breasts
(ii) Sense organs:
Tongue, Skin, Eyes, Nostrils, Ears
(iii) Functions:
- Tongue - Tasting
- Skin - Feeling (of touch)
- Eyes - Seeing
- Nostrils - Smelling
- Ears - Hearing
(b) (i) Compound:
A substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in a definite proportion
OR
A substance consisting of two or more elements that are combined chemically
(ii) Element:
A substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms
OR
Any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler one by a chemical reaction
(c) Particles:
Protons, neutrons and electrons
(d) (i) Energy changes for orange falling:
Potential → Kinetic → Sound + Heat
(ii) Energy changes for hammer hitting nail:
Chemical → Potential → Kinetic → Sound + Heat + Light
3. QUESTION 3
3. (a) (i) State three human activities that can cause an increase in soil erosion.
(ii) Give three ways of preventing soil erosion in agriculture.
(b) Describe briefly how a mixture of sand and common salt could be separated.
(c) (i) Define work.
(ii) State the unit of work.
(d) (i) Distinguish between heat and temperature.
(ii) State the units of heat and temperature.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3.(a) (i) Human activities causing soil erosion:
• Removal of cover crops
• Bush burning
• Ploughing along slopes
• Felling of trees
• Sand-winning
(ii) Preventing soil erosion:
• Planting of cover crops
• Planting more trees
• Practicing strip cropping
• Ploughing across slopes
• Terracing
(b) Separation method:
• Add water to the mixture and stir to dissolve the salt
• Pour the mixture through a filter paper in a funnel to separate the sand (residue) from the salt solution (filtrate)
• Heat the salt solution till all the water evaporates, leaving the salt crystals behind
• Dry the sand and the salt obtained
(c) (i) Work:
Work is done when an applied force moves an object in the direction of the force
OR
The transfer of energy, measured as the product of the force applied to a body and the distance moved by that body in the direction of the force
OR
Work = force × distance
(ii) Unit of work:
Joules or J
(d) (i) Distinction:
Heat: The energy possessed by a body that results in its hotness or coldness
Temperature: A measure of the hotness or coldness of the body
(ii) Units:
• Heat: Joules (J)
• Temperature: Kelvin (K), degrees Celsius (°C), or degrees Fahrenheit (°F)
4. QUESTION 4
4. (a) Name the organism that causes each of the following diseases:
(i) cholera
(ii) malaria
(iii) tuberculosis
(iv) ringworm
(b) State one method of preventing each of the diseases in (a) above.
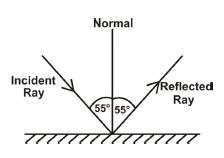
(c) A ray of light hits the surface of a plane mirror at an angle of 55°.
(i) Draw a ray diagram showing the normal, incident ray and the reflected ray.
(ii) What is the angle of reflection for the ray.
(d) State two properties of the image formed in a plane mirror.
(e) Write the chemical names of each of the following compounds:
(i) MgCl₂
(ii) FeS
(iii) NH₄OH
(iv) AgCl
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4.(a) Disease-causing organisms:
(i) Cholera: Bacteria (Vibrio cholerae)
(ii) Malaria: Protozoa (Plasmodium)
(iii) Tuberculosis: Bacteria (Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
(iv) Ringworm: Fungi (Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, and Microsporum)
(b) Prevention methods:
(i) Cholera:
• Eating hot meals
• Drinking clean potable water
• Washing hands with soap after visiting the toilet
(ii) Malaria:
• Sleeping under mosquito nets
• Applying mosquito repellents
• Burying empty cans
• Clearing bushy areas
• Spraying insecticides
• Clearing choked drains
(iii) Tuberculosis:
• Vaccination
• Ensuring adequate ventilation
• Avoid sharing cutlery/cups with infected persons
(iv) Ringworm:
• Keep skin clean and dry
• Avoid contact with infected persons/animals
• Avoid sharing personal items
(c) (i) Ray diagram description:
(ii) Angle of reflection:
90° - 55° = 35°
(d) Image properties:
- Same size as object
- Same distance from mirror as object
- Virtual
- Erect/upright
- Laterally inverted
(e) Chemical names:
(i) MgCl₂: Magnesium chloride
(ii) FeS: Iron(II) sulphide
(iii) NH₄OH: Ammonium hydroxide
(iv) AgCl: Silver chloride